
A year back, the government of India has taken an initiative to craft the country into a five trillion dollar economy towards the end of 2025, and one of the key requirements to turn this goal into a reality is revolutionizing the nation’s digital infrastructure. The country has already dug deep into enhancing the digital infrastructure, but experts claim that 5G services will be the key to a successful digital India. The question still remains when will 5G be available in the country in a full-fledged way. To answer this question, the Department of Telecommunications (DoT) recently stated that it will be available in mid or Q4 of 2022. The department also proclaimed that at first the services will be available in 13 cities and then the rest of the country will enjoy the benefits of this service. Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Chandigarh, Gandhinagar, Gurugram, Hyderabad, Jamnagar, Kolkata, Chennai, Lucknow, Pune, Delhi, and Mumbai are the first 13 cities to enjoy 5G.
5G has ultra-low latency through which it will offer speedier and seamless communication all over the world. This next-generation cellular technology will spearhead and empower modern cutting-edge technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and machine-to-machine communications. It will ultimately support a huge range of modern applications and use cases such as self-driving, facial recognition systems, connected devices, chatbots, and many more. In an interaction with the media, Nitin Bansal, managing director of Ericsson India said 5G will boost the economic growth in India and it will assist service providers in monitoring and managing the increasing data requirements of consumers in an efficient manner. The early use-cases for 5G in the country are speculated to be fixed wireless access (FWA) and enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) that would aid in solving the troubles of limited fixed broadband services and perk up the data experience while on the go.
Now, the question is why India needs 5G badly in 2022. Satyajit Sinha, Senior Analyst at IoT Analytics told CircuitDigest, "The mobile operators will not only be assisted by 5G in monitoring the escalating data requirements of consumers, but also open the gates of revenues for them. 5G is already perking-up various industries in the world via commencing the fourth industrial revolution and by improving the network experience for several businesses and end consumers. In fact, 5G is speculated to spearhead the digital transformation of several sectors like education, energy and utilities, automotive, healthcare, manufacturing, and many more. Towards the end of 2030, the anticipated worth of 5G-enabled digitalization revenues in the country will reach around USD 17 billion.”

Source: Pixabay
How 5G will Lead India’s Digital Transformation by 2025
People in the remote corners of the country enjoyed the benefits of 4G in a better way, but at the same time, we cannot overlook the imperativeness of broadband connectivity for the financial and social enhancement of the nation. The lockdowns have underlined the significance of connectivity in every aspect of our life starting from introducing work from home, the commencement of online trade on a large scale, online education and most importantly, connecting people. The digital India initiative that centers on empowerment depends massively on connectivity and the mobile networks in the country continue to offer its services on that promise.
According to telecom experts, 5G is not only about some giga-bit data speeds. In the beginning, the fuss was about the speed of the 5G deployments, but it is going to transform our life the way we live and play, and work. The fundamental shift from 4G to 5G would be multi-dimensional and the immensity is much bigger than the shift from 3G to 4G. 5G will not only offer a wide range of new-fangled spectrum to be put to use, but it will also become more effective than 4G in the spectrum already in utilization. It can accumulate more data than 4G for the same volume of spectrum.
5G will fetch a huge transformational shift in the teaching domain with remote learning coupled with teaching in the classroom to intelligently escalate the educational efficacies. In India, where 70 percent of people live in rural areas it becomes too difficult to provide top-notch education to everyone manually. Hence, 5G backed by ultra-low latency and higher speed will provide proper education and cater to a wider population. Then, when it comes to smart cities and smart homes, devices furnished with sensors communicating to each other will turn into key equipment. For homes specifically, people might witness cutting-edge AI backed personalization, automated grocery lists, tracking electronic devices, and automated deployment of everyday routines. In terms of smart cities, 5G has the potential to offer smart metering systems and smart electricity grids, safety mechanisms, waste disposal systems, and smart traffic management.
Highlighting the importance of 5G in India’s digital transformation, Lt. Gen Dr. S.P Kochhar, Director General, Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI) said, "With the Prime Minister’s inauguration of the 5G testbeds, the industry is on the pathway towards indigenization of 5G and it opens up opportunities for various other new-age technologies such as big data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), etc. which will drive major innovations across industries – Manufacturing, Supply Chain, Healthcare, Transportation and bring us closer towards our vision i.e. Digital India. A couple of impediments like cutting-edge infrastructure and Right of Way (RoW) policies being discussed thoroughly among the regulatory bodies and the unveiling of Gati Shakti Sanchar Portal is yet another promising move for the Indian telecom industry. Industry associations like COAI are working closely with the regulatory bodies and service providers to navigate through the challenges and further amplify the initiatives launched by the Government of India.”
COAI also added that 5G network rollout is expected to add $450 billion to the Indian economy, increasing the pace of development and creating jobs. Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently said that 5G technology will bring positive change in the governance of the country, ease of living, and ease of doing business, especially newer opportunities for the B2B businesses.
Current Role of 5G in Averting Security Risks for IoT Devices
In the coming few years, the volume of IoT connections is expected to augment all over the world, which is about 25.2 billion towards the end of 2025, predicts GSMA Intelligence unit. The report also highlighted that over 3.1 billion out of the 25.2 billion would employ cellular technologies comprising low power wide area Mobile IoT networks. These days, a lot IoT backed devices utilizes wireless technology that comprises of short-range technologies, mostly utilizing unlicensed spectrum such as ZigBee, WiFi, and Z-Wave, and also and wide area cellular technologies, using licensed spectrum, such as LTE, 5G, and GSM. According to experts, cellular technologies that operate under a licensed spectrum offer a huge number of advantages for devices powered by IoT. These are mostly service enablement, sophisticated provisioning, and also device management. Apart from that cellular networks provide a huge international coverage and accurate reliability, performance, and security, which are required by the most promising and in demand IoT applications.
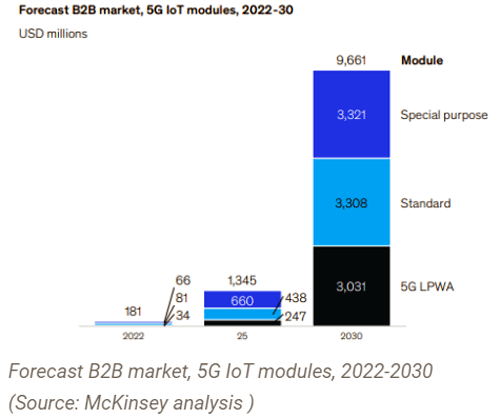
Now, talking from a security perspective, there could be 1.8 billion 5G connections by the end of 2025 as per the GSM association. Back in 2020, the 5G IoT market reached a value of USD 1.5 billion and is speculated to stand USD 40 billion by the end of 2026, at a CAGR of 72.9 percent over the time slot between 2021-2026. When 5G is amalgamated with IoT, it escalates the operational performance of several devices, but at the same time, high-end risks emerge. According to Satyajit Sinha, there is huge difference between deployment of IoT and deployment of 5G, which is regarding the standards that are available in either of these technologies.
Basically, the IoT powered devices are still highly unregulated and then follow no generic standards. An IoT device is crafted out of hardware and sensors that further connect a layer of software and the sensors. The software manages the hardware and sensor data and also does the computing. Apart from that, there is a communication interface available that permits connection to the 5G network. Now, crafting a basic security architecture is highly intricate as there are several ways to design, build, and utilize an IoT product.
The current risk assessments and methods are not perfectly designed to get to know about the IoT-based risks in a comprehensible manner. The devices will be on all the time and will be connected to the 5G network and ubiquitous. For instance, if you carefully look at smart home implementation, if there is a voice-enabled device, which is connected to an IoT-powered lock on the door, the person opens the door with his or her voice command. It is not fully secured because a thief who came to know the person has left the home, can come to the door and speak with the same voice command and can open the door. The point is there is absence of authentication at the IoT device. Now, another point to be noted is that 5G will still suffer from the 4G weakness, claims experts. Now, it is not possible to unleash a comprehensive 5G network all at once and in fact, in fewer places 5G is moderately deployed side by side a 4G software components and hardware for a certain time slot. Hence, to have a sturdy IoT security platform or a framework, it requires a multi-layered approach.
Conclusion
5G, after a constant transformation in the last two years, has grown from an emerging idea into a pervasive and important technology for mobile devices. The features of 5G that includes ultra-high density, ultra-high-speed, and ultra-low latency will be inserted into AI via wireless. The AI actions can be completed rapidly through 5G on the terminal side and it also perk-up personalized services, boost customer experience and decrease latency. In fact, 5G will also be benefited from the AI-enabled processing ability.
Highlighting the advantages, Neil Shah, Research Vice President at Counterpoint Research said, “The applications that are based on AI can respond in the accurate time to the data generated by the 5G networks, thereby offering new-fangled potentials for automation. Removing the conventional wireless algorithms with the help of proper machine learning, AI will be able to significantly decrease the price of manpower and enhance the total performance. It will also offer safety to the people’s everyday life, encouraging digital transformation, modernizing several commercial and industrial activities, and unleashing endless top-notch products and services.”





