Electronic Design Automation software or EDA software are tools used for designing circuits such as Integrated Circuits and PCBs. But before even designing the PCBs, engineers utilize software to check whether their electronics designs will perform as expected or not, and to do so they utilize the electronics circuit simulation software. Circuit simulation software is a tool developed for modeling and analyzing electronics circuitry. The mathematical models of different parameters of electronics components are used to replicate the performance and behavior of the circuit under different conditions. It is a fast and cost-effective method of designing and validating circuits, especially ICs before fabricating and testing them in the real world.
Electronics simulator packages usually comprise Schematic editor, PCB editor, Spice software which helps an engineer to perform complete design and analyze the performance of the circuit before physically building it, thus greatly improving efficiency while reducing the cost and time.
There are different types of software available for simulating analog, digital and mixed mode simulator capable of simulating circuits with varying accuracy, capabilities and have different instruments to do so. In this article we will compare CircuitMaker, LTspice, Multisim, KiCAD, EasyEDA, and PSIM, we will go through the costs, capabilities, and features of these products so that you can decide the best software for your usage.
Proteus
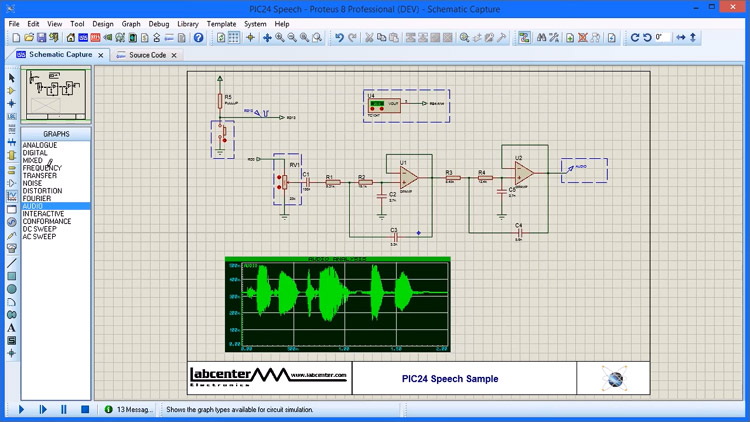
Proteus is an all-in-one software that is capable of doing simulation, designing circuits, and creating PCBs. The ISIS is the suite that is used for designing circuits and do real-time simulation. It allows real-time access even during simulation making it a convenient tool. The ARES is used for designing the PCB and has 3-D viewing features. The software came out around 3 decades ago and is considered one of the best by professional engineers. It has more than 15 million parts in the component library and offers features like differential pair routing, group length matching, remote front panel design for Arduino and Raspberry Pi microcontrollers, etc. This is one of the professional software with the availability of microcontrollers.
Most suitable uses:
The proteus is capable of performing all the simulation and design aspects of a project and with such a long time in the industry, it has refined almost all the features. But the one thing where it actually shines is the simulation part.
Cost:
The software is offered in 3 packages, Enterprise, Platinum, and Custom with price tags of $ 6592, $ 8003, and $ 248 respectively. The custom package by proteus gives a user an opportunity to completely customize their product and select only the essential features they need, the additional features can be added for an additional cost.
Pros of Proteus:
- More than 15 million components in the library
- Availability of microcontrollers such as PIC, Raspberry Pi, and Arduino, etc.
- Extremely prompt customer support
- The large variety of tools for analysis
- The user interface is easy to learn and use
Cons of Proteus:
- Cost, the packages are extremely expensive
- No free version of the software is available
To learn more about the software or to download it, you can visit their website.
Autodesk Eagle
Eagle is an EDA software from the company Autodesk. Eagle stands for Easily Applicable Graphical Layout Editor. It has a schematic editor, and PCB editor with the capability to design 16 layer PCBs with board sizes up to 4m^2. The software utilizes the free SPICE tool, Ngspice for circuit simulation. This software is extremely popular amongst hobbyists, small electronics makers and is used even in industry. The popularity amidst hobbyists and small firms gives it an edge in the DIY community. SparkFun Electronics and other open-source websites release Eagle files for boards designed in-house for the maker community. The layout is user-friendly and because of a large community, tutorials and resources are readily available.
Most suitable uses:
The Autodesk eagle is most suitable for small to mid-level complex projects. The large community makes it a great software for beginners as the availability of learning resources is high.
Cost of Eagle:
The Autodesk Eagle is offered in 3 variants, the Standard and Premium packages cost $100 and $500 annually or $15 and $60 monthly. There is a free version of the software which has limited capabilities in terms of sheet size, layers, and PCB board area.
Pros of Eagle:
- Free version with limited capability is available.
- Easy to use.
- Lot of resources and tutorials available due to a large community.
- 3-D modeling capability
Cons of Eagle:
- It doesn’t have signal and power integrity solution.
- Creating custom component is difficult
- Navigating library is complex and lacks components
To learn more about the software or to download it, you can visit their website.
CircuitMaker
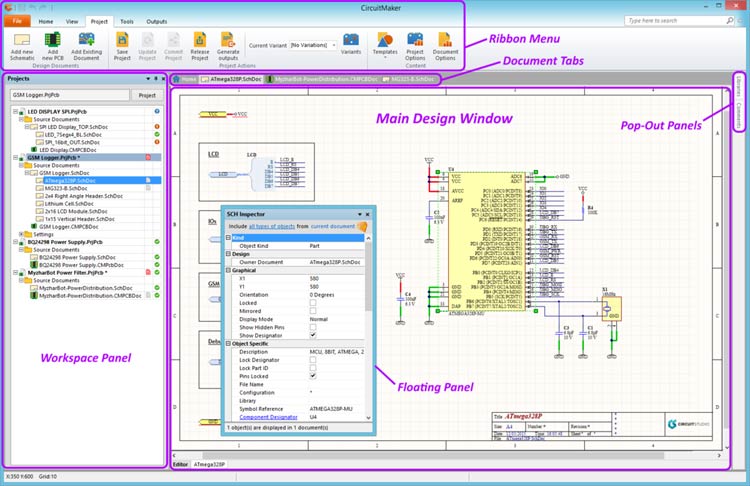
CircuitMaker is a free, web-based EDA software made by Altium. It borrows a lot of features from its more powerful elder brothers, Altium Circuit studio, and the Altium Designer. It has schematic designing and PCB editing capabilities but lacks simulating capabilities. Circuitmaker provides a multi-sheet schematic editor same as other Altium products and also features Altium’s proprietary 3D Design technology to visualize the PCB in a 3-Dimensional view. The software is capable of handling up to 16 layers with no restriction on the dimensions of the board. CircuitMaker also offers the auto routing feature which lets you route single nets or multi-net or even do manual routing with auto-complete. It also features concurrency editing which lets multiple users collaborate on a single project simultaneously. For freeware, Altium’s CircuitMaker is a really great product. The below image taken from the official documentations shows the layout of the schematic editor.
Most suitable uses:
Altium CircuitMaker is best suited for designing multilayer PCBs and a good component library makes it suitable for different electronics projects and its auto-routing feature makes it a good choice for even large projects.
Cost:
The CircuitMaker is a freeware with no cost whatsoever. It also doesn't have any non-commercial clause, i.e. you can use all the features of this software to make the commercial products without needing to pay any license fees making it a perfect solution for designers
Pros of CircuitMaker:
- The software is freeware.
- No non-commercial clause.
- The user interface is easy to use.
- It has a good component library.
- Powerful autorouting feature
- Good component wizard
- Supports importing projects from OrCAD, EAGLE, P-CAD, etc
Cons of CircuitMaker:
- There is no simulation tool available in the software.
- You can only have 5 private projects and data is saved over cloud
- Bugs and lags are more evident than many paid EDA tools.
- Only available for Windows operating system and not for Mac or any other OS.
To learn more about the software or use it online, you can visit their website.
NI MultiSim
National Instrument’s Electronics Design Automation tool NI Multisim is one of the most widely used tools for simulating electronics circuit. It has digital, analog and power electronics circuit design and simulation capabilities and it uses the original SPICE-based simulation software. Multisim has one of the highest tools and instruments available among its competitors and the simulations results are highly accurate and comparable to real-world testing. It also offers Digilent FPGA boards such as Basys and Nexys, these platforms can be programmed by exporting the digital logic diagrams created in Multisim in a raw VHDL format. It offers a PCB designing feature that is easy to use with a wide component availability in the library. It also features a very effective auto-routing feature. The user interface although have a mixed response due to its archaic looks and symbols which makes it difficult and time-consuming for new designers trying to enter the ecosystem. There is also a web-based platform called Multisim Live which lets you create and share circuits for free. Multisim is highly popular in Educational Institutes. A screenshot of Multisim live is shown in the image below.
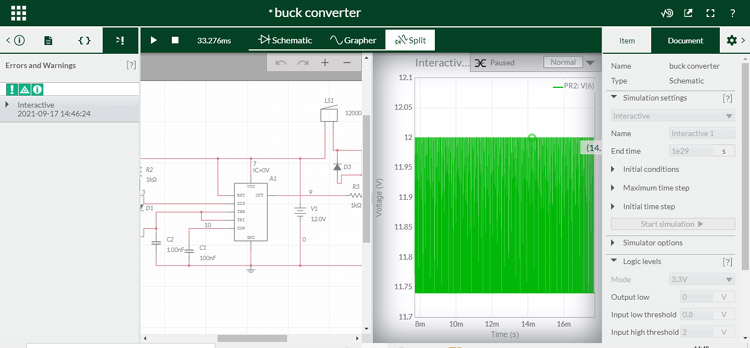
Most suitable uses:
It is mostly used in Educational institutes for teaching and doing research, it's mostly used for analyzing analog, digital, and power electronics circuitry.
Cost:
The NI multisim has 4 packages namely Education, Base, Full, and Power Pro priced at $628, $1869, $3267, and $4838 respectively. The base and the full package provide a partial component database with 47,000 and 49,000 components while the power pro package provides a full component database with over 55,000 components and an RF part selection limit of 17, 76 components for the cheaper options respectively while no such limit for the power pro package.
Pros of NI Multisim:
- Simulation results are very accurate
- Number of testing instruments available are high
- Over 55,000+ components available
- 35+ virtual instruments
- An online simulation software is available
Cons of NI Multisim:
- The user interface looks outdated and is difficult to navigate for some users
- Many microcontrollers and ICs missing in the library.
- Expensive
- Unavailability of complete components for the base package
- Only 4 out 35 virtual instruments available for the cheaper option.
To learn more about the software or to download it, you can visit their website. You can check the Multisim live by clicking here.
LTspice
LTspice is one of the most used simulation software in the industry. It derives its name from Linear Technologies, the previous name of Analog Technologies which developed this software. This software offers schematic capture and waveform viewer platform apart from the SPICE simulation it is known for. It also allows you to observe transient behavior on a cyclic basis and analyze the step-load response. Similar to CircuitMaker, it is a freeware with no restriction to features, the number of components, subcircuit, or limits in node but unlike the former which has no no-clause commercial usage clause, LTspice comes with some restrictions such as users are not allowed to compete with Analog devices products. The software uses an advanced algorithm which performs simulations faster than a lot of its paid counterparts with high accuracy.
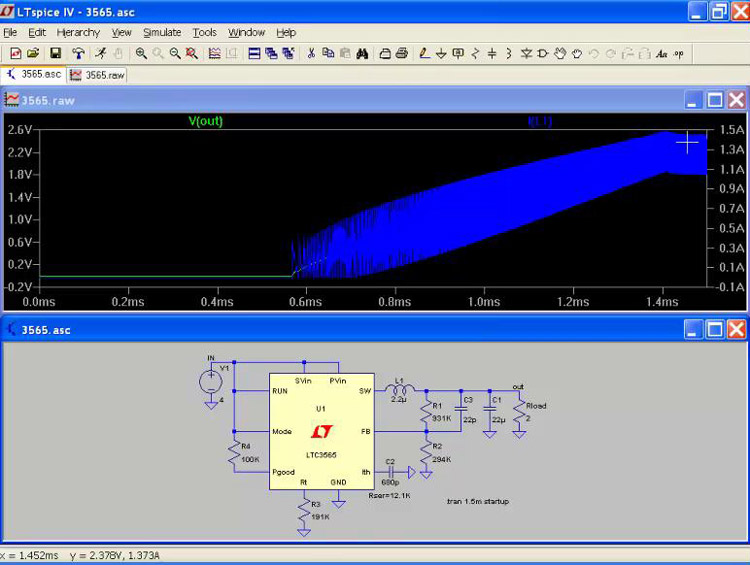
Cost:
LTspice is a freeware, all the features in the software are available to the users without any hidden cost.
Most suitable uses:
The software is useful for analyzing electronics circuits, power electronics circuits audio circuits, etc. The fast simulation and accurate results make it a good option for commercial product development without any expense.
Pros of LTspice:
- The software is completely free with no limitations to its usage.
- Accurate results
- Fast simulation
Cons of LTspice:
- Doesn’t have PCB editor
To learn more about the software or to download it, you can visit their website.
PSIM
PSIM is a specialized simulation software developed for simulating power electronics and motor drive simulation but also has the capability to simulate most other electronics circuitry. PSIM is developed by Powersim and uses trapezoidal rule integration and Nodal analysis as its main simulation algorithm. When compared to other software-based on SPICE, PSIM provides a much faster speed and models which are rarely available in most other software such as Multi-level converters, and models for renewable energy systems. It also provides an automatic embedded code generator and has an option for thermal simulation which computes switching and conduction losses of switching devices.
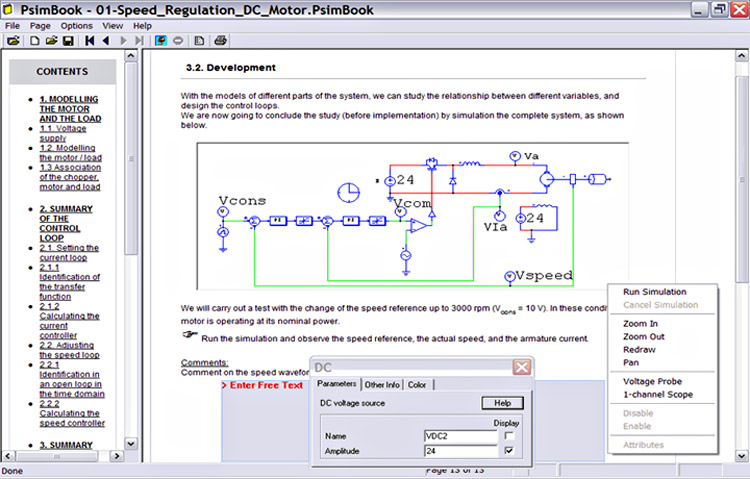
Most suitable uses:
This software is most suitable for power electronics simulation, it is also capable of simulating motor controllers, motor drivers, inverters, etc. This is a great software for people in the Renewable energy industry or engineers working on storage systems, grids, or even powertrain of vehicles.
Cost:
The company offers 3 packages, Student, Annual Academic License, and Education pro package retailing at $99, $300, and $1500 respectively. The Education pro package is similar to an annual academic license with a lifetime license validity. The student license having the max circuit size capped at 60 elements while the other 2 having no such restriction. The student license also lacks thermal modeling and many core features such as code generation or links with other software.
Pros of PSIM:
- Fast and accurate simulation
- Thermal simulation capability
- Wide choice of models for power electronics
- Various models specifically for renewable energy systems and energy storage systems.
- Affordable software
Cons of PSIM:
- It is a paid software, for basic electronics circuits many freeware are more suitable.
- Less testing equipment compared to other competitor software like multisim.
To learn more about the software or to download it, you can visit their website.
EasyEDA
EasyEDA is a fully functioning web-based EDA tool and simulation software. This software doesn’t have a non-commercial license, making it a great tool for students and normal users. It is a great tool for basic to intermediate users which provides an easy to adapt user-interface and ability to generate BOM or convert your schematics to a PCB as it also has a PCB editor tool. You can then download the gerber files to get your PCB fabricated. It was essentially made for the maker community as a freeware thus provides all the essential features in its free web-based tool.
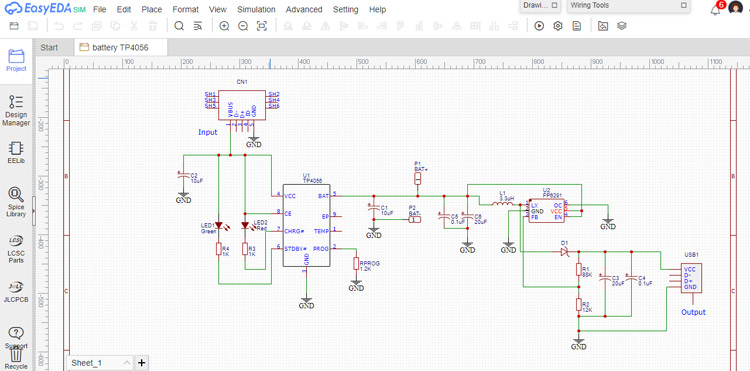
Cost:
In terms of pricing, this is one of the cheapest software available in the market apart from the freeware software. The EasyEDA has 3 plans, a free package which is a freeware, a professional pack that costs $4.9 a month, and the Enterprise pack which costs $9.9/ month. The only difference among the three packages is that you don’t get advertisements in the paid versions and with the Enterprise package you also get improved team management features.
Best used:
The online software is best suited for new and intermediate users, its easy and clean interface makes learning the software very easy but the lack of features and capabilities make it incompatible for the power users.
Pros of EasyEDA:
- Inexpensive
- Easy to navigate user-interface
- No non-commercial licensing
- Unlimited private project
- No need to install any software
Cons of EasyEDA:
- The main drawback of EasyEDA is its limited features
- Internet connection is required to work on it
- Limited components
To learn more about the software or use it online, you can visit their website.
KiCAD
KiCAD is another free EDA software that even lets users modify the software to their liking by modifying the source code. It has a very simple user interface and getting started with KiCAD is fairly simple. The schematic editor is called the Eeschema. When it comes to the component library, KiCAD has a lot of components available but navigating library is a bit confusing as it doesn’t have an atomic library, but one library for symbols and another for component making it a bit confusing for the beginner. The KiCAD has a very powerful 3D viewer which lets you visualize the PCB in a 3D mode, but you don’t get an auto-router feature installed in the software, instead, you need to download the layout editor to use this feature. The KiCAD is capable of running simulation using a free SPICE tool called ngspice, but it is complicated for a new user.
Cost:
The software is a freeware with no limitation to its usage.
Best use case:
The KiCAD is good for making a PCB layout as it doesn’t have any limitation on the board size, number of layers, and number of pins. The availability of a SPICE tool makes it a very lucrative package.
Pros of KiCAD:
- Free software with no limitation
- Easy to understand user interface
- Powerful 3D viewer
- No limitation to the size of the board or layers
Cons of KiCAD:
- No auto-routing features and requires add-ons for that
- Complex component library menu
To learn more about the software or to download it, you can visit their website.
Final Thoughts
There is a lot of simulation and EDA software available in the market. Every software has some pros and cons, some are extremely accurate and have a lot of features but require time to get used to them and are costly while there are some freeware which are giving close competition to the paid software. Some software like the PSIM are really good for power electronics simulation while NI’s Multisim has a lot of virtual testing equipment for testing even the RF circuits, etc. Thus, a one-fit solution is not possible for all the cases, and depending on the project’s requirement and complexity a software has to be chosen.





