Industry 4.0 is the fancy name given to the fourth Industrial revolution. In this article, we will discuss about what is Industry 4.0 and how is it going to enhance the future of Industries? Why such a buzz about it? Why failing to adopt it may kill your business? Let us take a look. It is sometime spelled as Industrie 4.0, this is the German translation of Industry so both can be used interchangeably.
Industrial Revolutions
Almost every review paper, white paper or blog that you read about Industry 4.0 would have a piece about former industrial revolutions. We will also discuss briefly about previous industry revolutions.
First Industrial Revolution
First Industrial revolution is the transition from manual labor to steam engine where the mechanical advantage of steam engines was leveraged to lessen the human labor.
Second Industrial Revolution
Advent of electricity into industries marks the second Industrial revolution. Electrical motors and analog systems replaced the steam engine. There was little to no manual labor involved. Mass production assembly lines were introduced during this period.
Third Industrial Revolution
Computers, PLC and electronics in factories and industries made it possible for humans to program the electrified machines and third industrial revolution was born. It eventually paved way for automation.
What qualifies to be an industrial Revolution?
According to Joel Mokyr, a renowned economic historian “An Industrial Revolution can be considered as a system of macro inventions that generates events that change society in a definitive and pragmatic way, regardless of the supporting scientific basis”. All the three Industrial revolution that the world has seen comply with the above definition. Does the fourth Industrial Revolution “Industry 4.0” do the same? Let’s find out…
What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 was coined in 2011 by a German initiative by the Federal government in association with some of the universities and private firms to increase productivity and efficiency in the manufacturing sector like Make in India.
Industry 4.0 is the integration of data, artificial intelligence, machinery and communication to create an efficient industrial ecosystem that is not just automated but intelligent.

Dirk Salma, the director of business development at Bosch Software Innovation GmbH said “It’s not only the things that we manufacture become more and more intelligent and connected but its also that the manufacturing process itself can really leverage these technologies and concepts in Industry 4.0” in his keynote at NEXT Conference. I love this definition and would like to reframe it as “Industry 4.0 is the process of embedding intelligence and connectedness in manufacturing and supply chain to provide satisfying products and services”.
Americans prefer to call this concept- smart factory and Europeans call it- Industry 4.0 (Germans came up with the term). So don’t be baffled when you hear terms like smart factory and Industrial IOT. They all refer to Industry 4.0 as there is no consensus about how we call it.
A Cyber physical system plays a vital role in Industry 4.0 and is changing the face of the industry. It again is a fancy name for the physical systems with electronics embedded in them for making them intelligent.
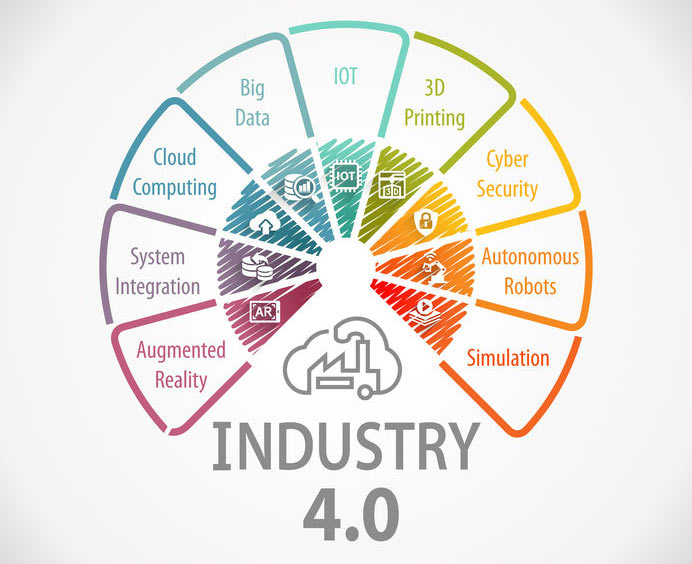
The Nine Pillars of Industry 4.0
The following nine advancements are familiar concepts used in industries especially in manufacturing. Integrating them where they are used individually at present and implementing the lacking concepts empower the factories to be intelligent and that is what Industry 4.0 is all about. To understand the implementation practically, let us visualize a simple PCB manufacturing facility to understand these nine pillars. As we learn about the nine pillars, we will assume that we have a PCB manufacturing facility and shall try to apply the technology to the facility and witness the regular factory turn into a smart one.
1) Big Data and Data analytics
Data analytics, once an IT application is now penetrating into manufacturing and supply chain industry. Power of data analytics and pattern recognition can be harnessed in the manufacturing industry to reduce downtime and wastages.
In our facility, data can be collected at different levels of manufacturing process. If a PCB or a batch of PCBs is found to be faulty, their manufacturing data can then be retrieved and comprehensively evaluated to arrive at a pattern. Process involving those patterns can be redesigned and re-evaluated to reduce wastage and increase productivity.
Predictive maintenance can be carried out based on the data collected. This is cost-efficient and safer than the conventional routine maintenance method.
2) Simulation
A simulation, in present day is used to design components that are manufactured. In Industry 4.0, it can be used to simulate a virtual environment of the factory itself with the real time data and analyze the productivity before a change in the factory can be made. This helps engineers to visualize the design in a much better manner consequently helping them identify problems and obstacles in the early stage.
Consider that in our manufacturing facility, we have three robots to solder the PCBs. With this in mind, our sales team promises the clients that their order will be delivered in 3 weeks. Unfortunately, one of the older robots faces some technical glitch with deadline in 10 days. Simulations with different speed of work can be operated to arrive at an optimum speed at which the robots can operate without frying themselves up and meet the deadline. Else, we either end up missing the deadline by operating two robots at normal speed or run the risk of damaging the working robots with trial and error method.
3) Horizontal and Vertical Integration
Horizontal integration takes networking among the cyber-physical systems and enterprise systems to an unprecedented level. Every device and system at the same level of manufacturing in the same facility or the other is connected with each other. As this enables communication between systems in different facilities, jobs can be planned and adjusted by the machines themselves. Downtime at a facility can be compensated by overtime at another facility with no human intervention whatsoever
Vertical integration makes it even better. Every system and humans at all hierarchy has all the data with required abstraction. Notable challenge faced in vertical integration is the communication protocol. It is insane to expect all the systems to talk the same language which they obviously don’t. This can be overcome by using interfaces; Quite a painful job but worth the work.
4) Industrial Internet of Things
You would have heard about the concept of IOT, I bet. An ecosystem in which all the sensors and actuators with the ability to function separately and communicate with every other element is called IOT. Industrial IOT is the same but with increased ruggedness to survive the harsh environments of the industry.
Why should the components communicate with each other? What actually is the need to do so?
Consider that our factory has run out of solder. There is no point in pushing out batches of printing circuit boards when there is no solder lead available to integrate the components. Instead of a human stopping the process, solder lead holder enabled with sensors could prompt the inventory team to buy more solder in prior. If the inventory team had failed to refill, the printer (etcher) can be turned off or can go in idle mode after receiving a signal from the solder holder.
5) Autonomous Robots
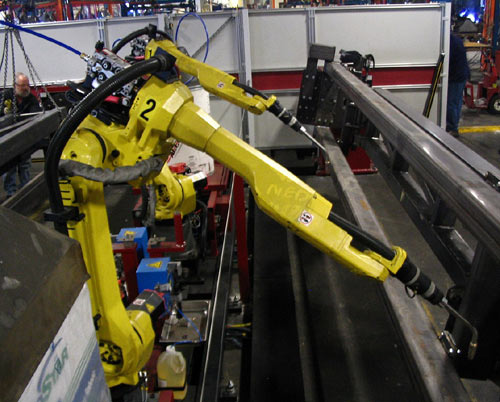

Autonomous robots transfer raw materials, half-finished and completed goods in an easier, faster and smarter way. They operate based on a complex logic algorithm, meaning they don’t require any preset path to carry out their duties.
These robots catalyze the manufacturing process. The amount of time that can be gained and latency that can be cut down is equal to the amount of time taken to program controlled robots. Unlike the conveyor belt, it is portable and its duty can be varied.
Tesla Motors’ Gigafactory is an example. They house Autonomous Indoor vehicles (AIVs) to transfer materials between workstations. The vehicles can carry payloads up to 130 lbs., and can even charge their own battery without intervention. They have line follower robots too which move in a defined path. So the line-follower robot you made for your project has applications after all.
In our case of PCB manufacturing factory, these autonomous robots can be used to move the PCBs, once fully completed to the packaging area. If the manufacturing facility is revamp and the packaging location is changed, just a change of destination in the robot’s system would suffice to operate normally.
6) The Cloud
Cloud is a remote system that can be accessed provided from anywhere using the internet. There are a lot of cloud services available today of which notable are IaaS, PaaS, SaaS. Communication among machines themselves and between machines and humans are hugely backed by cloud services.
Amazon.com Inc. is the best example. A consumer gets updated about the whereabouts of his order in real time. This is not a one-to-one message. Once your package has arrived at the warehouse, information is updated in cloud which is then notified to you. Every time you check for your package’s present location, get query is executed in real time to let you know about your package.
This can be integrated in PCB factory and supply chain. Under the topic of Data analytics we already have discussed about placing sensors in different locations of manufacturing. These can be stored in the cloud which is available for anyone with credentials. They can be accessed by employees to take required actions there and then as necessary. Customers would be extra happy and satisfied to view the real time data of their product being manufactured unless we have delays due to technical glitches.
7) Cyber Security in Industry 4.0
Cyber security becomes the talk of the town since the dawn of Information technology. The greatest nightmare of any information technology firm is having their server and data hacked. Preventing such a catastrophe and safeguarding the data and performance of the server is the sole purpose of cybersecurity.
Very fancy and futuristic. But how is it going to affect a small firm that produces Printed Circuit Boards?
As more and more components get connected and one device’s action is based on the output of another device, more operational decisions are decentralized, more security concerns are raised.
Think of the consequences if someone hacks into our system and changes the PCB design and erases his digital footprints. Earlier, sole way to steal the PCB design would be to physically log into the machine that has the same. Connectivity makes the system vulnerable to anyone in the same network to access the designs.
This is where cyber security comes into play. Theft and intentional obliteration can be checked through the same. Integration of the system with cloud by itself advocates the need for cyber security.
8) Augmented Reality

Augmented Reality based systems are storming the technology industry. Few years ago they found their applications only in flight simulators. Today remote repair instructions can be sent to literally any part of the earth with internet accessibility. It helps technicians to enhance their skills by practicing high end repairs and maintenance over and over again using augmented reality.
Consider for example, we have an equipment worth of some million dollars needing some form of maintenance. Before carrying out the job on the actual equipment, a training session can be conducted. Once the technician is confident enough to be impeccable, he can do the same with the actual equipment. It is a win-win situation. We don’t lose our equipment; Technician does not get embarrassed messing up the job.
9) Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing
Companies are already using additive manufacturing techniques like 3D-printing to make prototypes and Proof of concepts. The flexibility of Industry 4.0 allows us to design complex designs which are nearly impossible with conventional manufacturing processes.
Most of the conventional manufacturing processes are subtractive manufacturing which includes wastage of raw materials. Additive manufacturing drastically reduces if not totally eliminate the wastage of raw materials.
A company named "made in space" has plans to construct satellites in space. This has a lot of added advantages. Densely packed raw materials can be sent to space where they can be used to construct objects of bigger volume. Satellite designs, that were cost efficient but too fragile to survive the rocket launch forces, can be manufactured in outer space.
Why should you adopt Industry 4.0?
Like it or not, but the use of Industry 4.0 is growing rapidly and your competitors are adapting it. Not all the nine technological pillars are required in all industries and fields but failing to make the most of it makes your competitors stronger.
Giants like Amazon, Tesla motors, Lockheed Martin, Hyundai, and Boeing are busy transcending to the next level which is Industry 4.0. Staying stagnant may not just inhibit your success but kill your business. It is simple as that. Grow or Perish.
All the customers look for smarter manufacturing, connected supply chain and value added product & service, which can be easily deliverable through Industry 4.0. It is out there to be used. So be the part of Industry 4.0 revolution and become the part of new era.