In this 555 timer Astable calculator, enter the values of timing capacitor C and timing resistors R1 & R2 to calculate the frequency, period and duty cycle. Here the time period is the total time it takes to complete one on/off cycle (T1+T2), while Duty cycle is the percentage of total time for which the output is HIGH.
555 Timer Astable Calculator Description
When a 555 timer is operating in Astable mode we obtain a pulse on the output pin whose ON time (Time high) and OFF time (Time low) can be controlled. This controlling can be done by selecting the appropriate values for the Resistor R1,R2 and capacitor C1. The circuit diagram to operate the 555 IC in Astable mode is shown be

The above circuit can be used to produce a square wave in which the high time (T1) and low time (T2) can be calculated. This method can be used to generate clock pulses for Microcontrollers/Digital IC’s or blink an LED or any other applications where specific time intervals are needed. The output wave obtained from pin 3 is shown with markings below
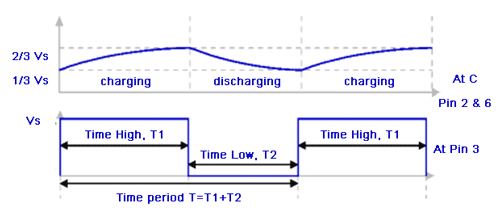
The time axis T is measured in seconds and the Voltage axis is measured in Volts. As said earlier how long the pulse stays high, how long the pulse stays low and the frequency of the pulse can be calculated using the value of components R1,R2 and C1 shown on the circuit diagram above.
The above 555 timer Astable calculator can be used to calculate these values, but to understand its working we need to know the following formulas based on which the calculator works.
|
Parameter |
Formulae |
Unit |
|
Time High (T1) |
0.693 × (R1+R2) × C1 |
Seconds |
|
Time Low (T2) |
0.693 × R2 × C1 |
Seconds |
|
Time Period (T) |
0.693 × (R1+2×R2) × C1 |
Seconds |
|
Frequency (F) |
1.44 / (R1+2×R2) × C1 |
Hertz (Hz) |
|
Duty Cycle |
(T1/T)×100 |
Percentage (%) |
Note: These units are applicable only when R1 and R2 is in ohms and Capacitor is in Farads
It might be hectic to try different values of Resistor and capacitors to arrive at you desired Time interval and Frequency. So, always keep these below tips in head while selecting your values
TIPS:
- Period(T) and Frequency(F) are inversely proportional
- Increase in C1 will decrease Frequency (F)
- Increase in R1 will increase High Time (T1) but will not alter low Time (T2)
- Increase in R2 will increase High Time (T1) and also increase low Time (T2)
- So, always set T2 first and then T1
- Increase in R2 will decrease duty cycle
Once we have all these details, we can get to know the complete properties of the output wave. To get used to the formulas lets calculate the value for parameters using these formulas for the circuit diagram given above.
Model Calculation
In our circuit diagram the value of Resistors R1 and R2 is 1K and 100K respectively, the value of capacitor C1 is 10uf.
So, R1 = 1K; R2 = 100K and 10uF
Or can be written as R1=1000 Ohms; R2=100000 Ohms, C1=0.00001 Farads
The Time high (T1) is the amount of time during which the pulse stays high (5V) in the output wave. This can be calculated as
Time high (T1) = 0.693 × (R1+R2) × C1
= 0.693 × (1000 +100000) × 0.00001
= 0.699 seconds
T1 = 699 milliseconds
The Time low (T2) is the amount of time during which the pulse stays low(0v) in the output wave. It can be calculated as
Time low (T2) = 0.693 × R2 × C1
= 0.693 × 100000 × 0.00001
= 0.693 seconds
T2 = 693 milliseconds
The time Period (T) is the sum of Time low and Time high. Changing wither Time high or time low will affect the Total time period T
Time Period (T) = 0.693 × (R1+2×R2) × C1 or (T1+T2)
= 0.693 × (1000 +2×100000) × 0.00001 or (0.699+0.693)
T = 1.393 seconds
As we all know frequency is just the inverse of time. There are certain applications like a servo motor control where the pulse has to be in a certain frequency for the driver circuit to respond. The frequency can be calculated as
Frequency (F) = 1.44 / (R1+2×R2) × C1 or (1/T)
= 1.44 / (1000 +2×100000) × 0.00001 or (1/1.393)
F = 0.718 Hertz
Duty Cycle is always given in terms of percentage, if high time is equal to low time then the pulse has 50% duty cycle and if the off time is zero then it has 100% duty cycle. We can calculate the duty cycle as.
Duty Cycle = (T1/T) × 100
= (0.966/1.393) × 100
DC = 50.249 %
Likewise we can calculate these parameters for any value of Resistor and Capacitor. Using the 555 timer calculator will really come in handy when you are designing a new circuit for your project.

