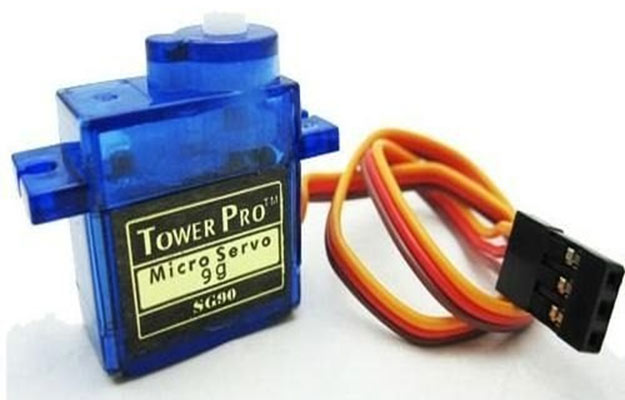

What is a Servo Motor?
A servo motor is a type of motor that can rotate with great precision. Normally this type of motor consists of a control circuit that provides feedback on the current position of the motor shaft, this feedback allows the servo motors to rotate with great precision. If you want to rotate an object at some specific angles or distance, then you use a servo motor. It is just made up of a simple motor which runs through a servo mechanism. If motor is powered by a DC power supply then it is called DC servo motor, and if it is AC-powered motor then it is called AC servo motor. For this tutorial, we will be discussing only about the DC servo motor working. Apart from these major classifications, there are many other types of servo motors based on the type of gear arrangement and operating characteristics. A servo motor usually comes with a gear arrangement that allows us to get a very high torque servo motor in small and lightweight packages. Due to these features, they are being used in many applications like toy car, RC helicopters and planes, Robotics, etc.
Servo motors are rated in kg/cm (kilogram per centimeter) most hobby servo motors are rated at 3kg/cm or 6kg/cm or 12kg/cm. This kg/cm tells you how much weight your servo motor can lift at a particular distance. For example: A 6kg/cm Servo motor should be able to lift 6kg if the load is suspended 1cm away from the motors shaft, the greater the distance the lesser the weight carrying capacity. The position of a servo motor is decided by electrical pulse and its circuitry is placed beside the motor.
Servo Motor Working Mechanism
It consists of three parts:
- Controlled device
- Output sensor
- Feedback system
It is a closed-loop system where it uses a positive feedback system to control motion and the final position of the shaft. Here the device is controlled by a feedback signal generated by comparing output signal and reference input signal.
Here reference input signal is compared to the reference output signal and the third signal is produced by the feedback system. And this third signal acts as an input signal to the control the device. This signal is present as long as the feedback signal is generated or there is a difference between the reference input signal and reference output signal. So the main task of servomechanism is to maintain the output of a system at the desired value at presence of noises.
Servo Motor Working Principle
A servo consists of a Motor (DC or AC), a potentiometer, gear assembly, and a controlling circuit. First of all, we use gear assembly to reduce RPM and to increase torque of the motor. Say at initial position of servo motor shaft, the position of the potentiometer knob is such that there is no electrical signal generated at the output port of the potentiometer. Now an electrical signal is given to another input terminal of the error detector amplifier. Now the difference between these two signals, one comes from the potentiometer and another comes from other sources, will be processed in a feedback mechanism and output will be provided in terms of error signal. This error signal acts as the input for motor and motor starts rotating. Now motor shaft is connected with the potentiometer and as the motor rotates so the potentiometer and it will generate a signal. So as the potentiometer’s angular position changes, its output feedback signal changes. After sometime the position of potentiometer reaches at a position that the output of potentiometer is same as external signal provided. At this condition, there will be no output signal from the amplifier to the motor input as there is no difference between external applied signal and the signal generated at potentiometer, and in this situation motor stops rotating.
Interfacing Servo Motors with Microcontrollers:
Interfacing hobby Servo motors like s90 servo motor with MCU is very easy. Servos have three wires coming out of them. Out of which two will be used for Supply (positive and negative) and one will be used for the signal that is to be sent from the MCU. An MG995 Metal Gear Servo Motor which is most commonly used for RC cars humanoid bots etc. The picture of MG995 is shown below:

The color coding of your servo motor might differ hence check for your respective datasheet.
All servo motors work directly with your +5V supply rails but we have to be careful on the amount of current the motor would consume if you are planning to use more than two servo motors a proper servo shield should be designed.
Controlling Servo Motor:
All motors have three wires coming out of them. Out of which two will be used for Supply (positive and negative) and one will be used for the signal that is to be sent from the MCU.
Servo motor is controlled by PWM (Pulse with Modulation) which is provided by the control wires. There is a minimum pulse, a maximum pulse and a repetition rate. Servo motor can turn 90 degree from either direction form its neutral position. The servo motor expects to see a pulse every 20 milliseconds (ms) and the length of the pulse will determine how far the motor turns. For example, a 1.5ms pulse will make the motor turn to the 90° position, such as if pulse is shorter than 1.5ms shaft moves to 0° and if it is longer than 1.5ms than it will turn the servo to 180°.
Servo motor works on PWM (Pulse width modulation) principle, means its angle of rotation is controlled by the duration of applied pulse to its Control PIN. Basically servo motor is made up of DC motor which is controlled by a variable resistor (potentiometer) and some gears. High speed force of DC motor is converted into torque by Gears. We know that WORK= FORCE X DISTANCE, in DC motor Force is less and distance (speed) is high and in Servo, force is High and distance is less. The potentiometer is connected to the output shaft of the Servo, to calculate the angle and stop the DC motor on the required angle.
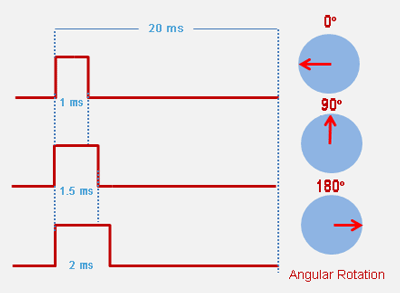
Servo motor can be rotated from 0 to 180 degrees, but it can go up to 210 degrees, depending on the manufacturing. This degree of rotation can be controlled by applying the Electrical Pulse of proper width, to its Control pin. Servo checks the pulse in every 20 milliseconds. The pulse of 1 ms (1 millisecond) width can rotate the servo to 0 degrees, 1.5ms can rotate to 90 degrees (neutral position) and 2 ms pulse can rotate it to 180 degree.
All servo motors work directly with your +5V supply rails but we have to be careful about the amount of current the motor would consume if you are planning to use more than two servo motors a proper servo shield should be designed.
To learn more about servo motor working principle and practical uses, please check below applications where controlling of servo motor is explained with the examples:
appreciation
hi,
thank you so much for your support
I'm in the industry, working with servo motors I needed to learn their
operation and controls
Request for Servo Motor PDF
Hello Sir,
I request for Servo motor PDF if you have any, I am learning about them.
Thanks
Help me to understand more about servo am in certain industry..
Thanks for your services
Electrical technology
The production of rotating magnetic field and working principal of 3-phase induction motor
It depends on the servo motor
It depends on the servo motor, if it a small torque motor then with some force you should be able to rotate it when not powered. But for metal gear high torque motors the gear ratio will be very high so it get s a bit more hard to rotate the motor.
It is a different story when the motor is powered, even a small torque motor when powered and positioned in a degree (say 90*) then we will not be able to rotate it because the motor is constantly trying to keep the motor in that position 90* so when you rotate the motor by hand it will push it back to the previous position
Also it is not recommended to rotate the motors by hand because it will damage the gears inside
servo tensioners
I need to how servo motor works for wire tensioners ?






Principal & working